The Essential Machinery Behind Modern Retail Paper Bags
Release time:2025-05-29 Classification:Knowledge
In today's retail landscape, the shift towards sustainable packaging has placed the humble paper bag firmly back in the spotlight. But behind every sturdy, branded, or elegantly simple paper carrier used at checkout lies a sophisticated ecosystem of specialized machinery. This article delves into the world of retail paper bag equipment, exploring the core technologies and processes that transform rolls of kraft paper into the ubiquitous carriers we rely on daily.
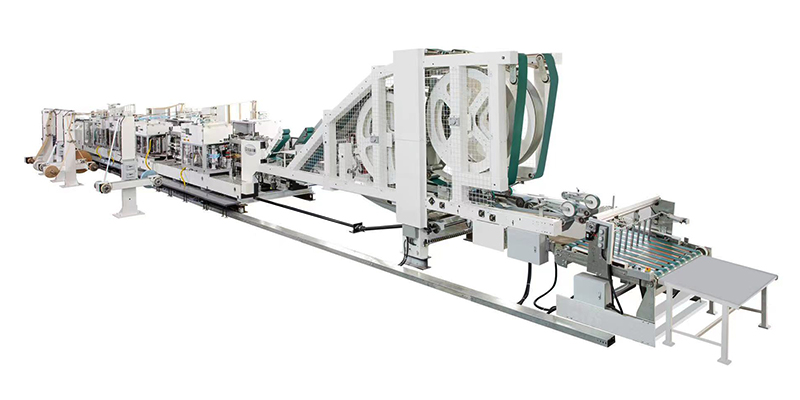
From Roll to Handle: The Production Journey
The transformation begins with large parent rolls of paper, typically kraft paper in varying weights (measured in GSM - grams per square meter) and potentially pre-printed or plain. The primary workhorse in retail paper bag equipment is the automatic paper bag making machine. These highly automated systems integrate multiple functions into a single, continuous production line:
- Unwinding & Feeding: Precision systems unwind the paper roll under controlled tension, ensuring smooth, consistent feeding into the machine. Sophisticated sensors monitor roll diameter and automatically splice new rolls onto running webs, minimizing downtime.
- Printing (Optional but Common): Many machines incorporate high-quality flexographic printing units. These allow retailers to apply logos, branding, promotional messages, or essential information directly onto the bag paper during production. Quick-change plate systems enable efficient runs of different designs.
- Creasing & Cutting: Rotary creasing wheels create precise fold lines for the bag's bottom and sides. Simultaneously, high-speed rotary knives cut the continuous web into individual bag blanks of the required height.
- Bottom Forming: This is a critical stage. Different machine types handle this differently:
- Pinch Bottom Machines: The most common for standard shopping bags. The machine pinches the bottom of the bag blank, applies adhesive, and folds it into a secure, flat seal.
- Square Bottom Machines: Used for bags needing a larger, more stable base (like gift bags). These machines form a distinctive block-shaped bottom through a complex series of folds and gluing.
- Automatic Pasted Valve Bag Machines: Primarily for heavier duty or bulkier items, these form a distinctive gusseted bottom with a pasted valve.
- Side Sealing: The open sides of the bag blank are folded and sealed, typically using hot melt adhesive applied precisely along the seam. Some designs might utilize stitching.
- Handle Attachment (Optional): For handled bags, this stage is crucial. Machines can attach various handle types:
- Die-Cut Handle Slotting: Punches slots into the bag body.
- Flat Paper Handle Application: Cuts and glues flat paper handles into the pre-punched slots.
- Twisted Paper Handle Application: Feeds, cuts, twists, and attaches the classic twisted paper handles. Precision glue application ensures handles are securely bonded.
- Ribbon or Rope Handle Attachment: Specialized units feed, cut, and attach fabric or rope handles.
- Folding & Counting: Finished bags are neatly folded (often flat for efficient storage and transport) and counted into precise stacks.
- Stacking & Bundling: Automated stackers collect the folded bags, and bundlers may wrap stacks in paper or plastic for protection before boxing.
Key Components and Technological Considerations
Modern retail paper bag equipment is characterized by:
- High Speed & Efficiency: Top-tier machines can produce thousands of finished bags per hour, making them essential for meeting large-scale retail demands cost-effectively.
- Precision Engineering: Accuracy in cutting, creasing, folding, and gluing is paramount for consistent bag quality, structural integrity, and appearance. Laser guides and servo motors ensure micron-level precision.
- Versatility: Many machines offer quick-change tooling and programmable settings to switch between different bag sizes, styles (pinch/square bottom, with/without handles), and paper weights with minimal downtime.
- Advanced Control Systems: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human Machine Interface) panels allow operators to monitor every aspect of production, adjust settings, diagnose faults, and track output data.
- Adhesive Application Systems: Reliable and precise hot melt glue systems are vital for strong, clean seams and handle attachment. Temperature control and nozzle design are critical factors.
- Robust Construction: Built to withstand continuous operation, these machines feature heavy-duty frames, hardened steel components, and durable wear parts.
- Safety Features: Comprehensive guarding, emergency stops, and safety interlocks protect operators around these high-speed machines.
Operational Factors for Retail Bag Production
Running efficient retail paper bag equipment requires attention beyond the machine itself:
- Paper Quality: Consistent paper properties (weight, tensile strength, moisture content, smoothness) are essential for trouble-free running and final bag performance. Variations can cause jams or weak bags.
- Adhesive Selection: Choosing the correct hot melt adhesive formulation for the specific paper type, bag style, and expected environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) is crucial for bond strength and longevity.
- Tooling Maintenance: Regular sharpening and replacement of cutting dies, creasing wheels, and other wear parts are necessary to maintain quality and prevent downtime.
- Operator Skill: Skilled operators are needed to set up machines efficiently, monitor production, perform routine maintenance, and troubleshoot issues swiftly.
- Sustainability Integration: Equipment designed to minimize paper waste (through optimized nesting), use energy efficiently, and handle recycled content papers effectively is increasingly important.
The Role in Sustainable Retail
Retail paper bag equipment is fundamentally enabling the move away from single-use plastics. By producing durable, recyclable, and often compostable paper carriers efficiently, this machinery supports retailers' environmental goals. The efficiency of modern equipment also contributes to sustainability by reducing energy consumption and material waste per bag produced.
The production of retail paper bags is far from simple. It relies on a complex array of highly engineered retail paper bag equipment, integrating precision mechanics, advanced controls, and material science. From unwinding massive paper rolls to applying the final handle, these automated systems work tirelessly to create the carriers that are both a practical necessity and a branding canvas for modern retailers. Understanding the capabilities and demands of this equipment is key for anyone involved in sourcing, producing, or utilizing paper bags in the competitive retail sector, ultimately supporting the delivery of functional, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing packaging solutions to consumers worldwide. The continuous evolution of this machinery promises even greater efficiency, versatility, and environmental performance in the years to come.






