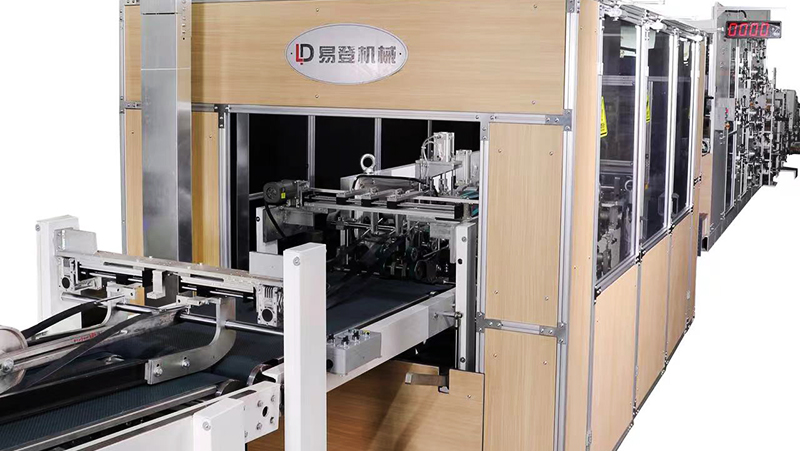
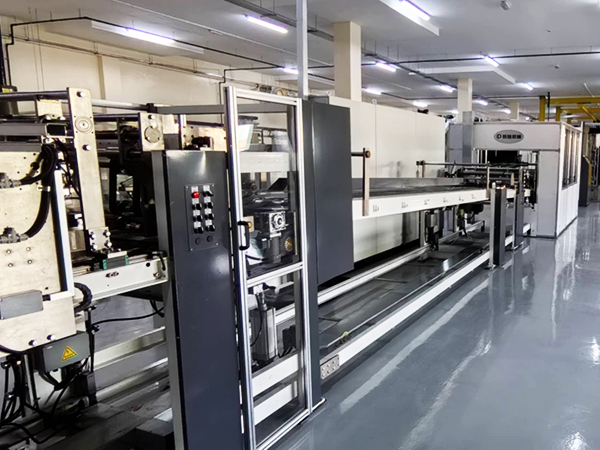
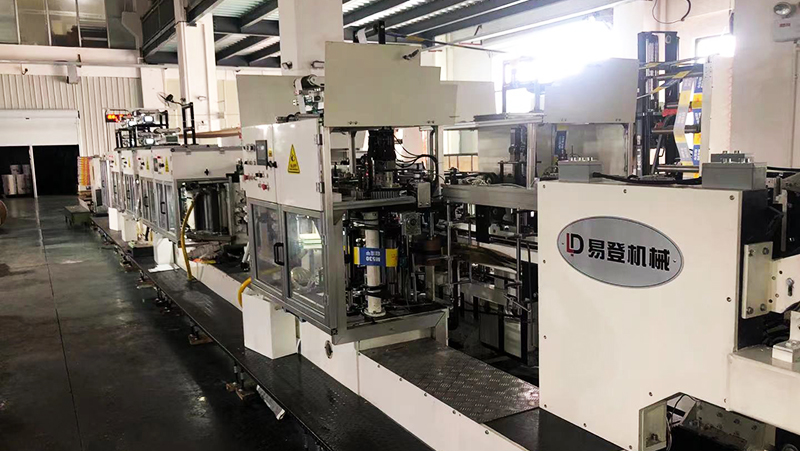
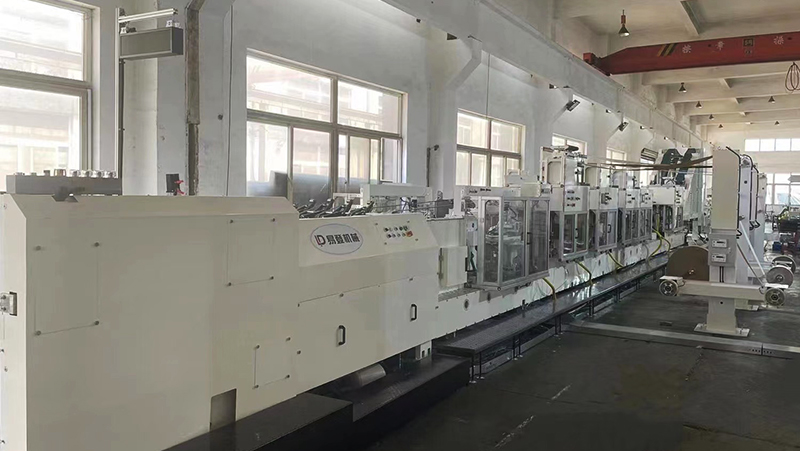
In the realm of industrial packaging, multiwall paper bags are indispensable for transporting and storing bulk materials such as cement, chemicals, food products, and agricultural goods. At the heart of their production lies the multiwall paper bag machine, a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to automate and optimize the creation of durable, multi-layered paper bags. This article delves into the functionality, components, and significance of these machines in modern manufacturing.
What is a Multiwall Paper Bag Machine?
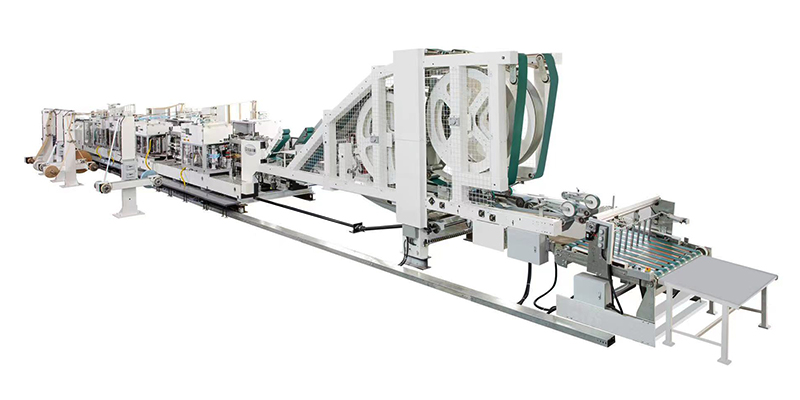
A multiwall paper bag machine is an automated system engineered to produce multi-layered paper bags, typically comprising 2–6 plies (layers) of kraft paper. These layers are bonded together to enhance strength, moisture resistance, and load-bearing capacity, making the bags ideal for heavy-duty applications. The machine integrates multiple processes—including paper feeding, printing, gluing, folding, and bottom sealing—into a seamless production line, ensuring high efficiency and consistency.
Key Components and Workflow
- Unwind Stands:
The process begins with rolls of kraft paper mounted on unwind stands. These stands feed multiple layers of paper into the machine simultaneously, allowing precise alignment and tension control. - Lamination System:
Layers of paper are bonded using adhesives or extrusion coating. This step enhances the bag’s structural integrity and barrier properties (e.g., water resistance). - Printing Unit:
High-speed flexographic or rotogravure printers apply branding, product information, or safety labels onto the outer ply. Custom designs can be achieved with precision. - Tube Formation:
The laminated paper is formed into a continuous tube using a forming shoulder. The edges are glued to create a seamless cylindrical structure. - Cross Cutting & Bottom Folding:
The tube is cut into predetermined lengths. A bottom-folding mechanism then creates the bag’s base, which is secured with glue or stitching. - Valve Application (Optional):
For filling powdery or granular materials, a valve is attached to the bag to facilitate controlled discharge. - Stacking & Packaging:
Finished bags are counted, stacked, and bundled for shipment.
Advantages of Multiwall Paper Bag Machines
- High-Speed Production: Capable of producing 100–300 bags per minute, these machines significantly boost output compared to manual methods.
- Customization: Adjustable parameters allow variations in bag size, ply count, print design, and valve types.
- Durability: Multi-layer construction ensures bags can withstand rough handling and harsh environments.
- Sustainability: Kraft paper is biodegradable and recyclable, aligning with eco-friendly packaging trends.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced labor costs and material waste enhance profitability.
Applications Across Industries
Multiwall paper bags are widely used in:
- Cement & Construction: For packaging cement, sand, and dry mixes.
- Chemicals & Fertilizers: Resistant to moisture and chemical exposure.
- Food & Agriculture: Suitable for grains, flour, sugar, and animal feed.
- Minerals: Transporting minerals like gypsum or bentonite.
Technological Innovations
Modern multiwall paper bag machines incorporate advanced features such as:
- PLC Control Systems: For real-time monitoring and adjustments.
- Automated Quality Checks: Sensors detect defects in printing, gluing, or folding.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduced power consumption through optimized motor systems.
- IoT Integration: Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion
The multiwall paper bag machine is a cornerstone of industrial packaging, combining speed, precision, and versatility to meet the demands of diverse sectors. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and automation, these machines will continue to evolve, driving innovation in eco-friendly and efficient packaging solutions. For manufacturers investing in bulk material handling, adopting a state-of-the-art multiwall bag machine is not just a choice—it’s a strategic imperative.
By streamlining production and reducing environmental impact, this technology underscores the future of packaging: smarter, stronger, and greener.